P(polynomial) type problems
In programming algorithms, P is a class of algorithms that can run and find a solution in polynomial time(in a deterministic way). Also, the solution can be validated in polynomial time.
Example: Addition of two numbers.
NP(non-deterministic polynomial) type problems
NP refers to the range of problems that may or may not be solved in polynomial time in a non-deterministic way(where the resulting state of a state change can be non-deterministic) but their solutions can be verified in polynomial time.
Non-deterministic :
Approach by taking guesses. No specific rule is followed when making a guess.
Alternative definition of NP :
A problem is called NP if its solution can be guessed and verified in polynomial time.
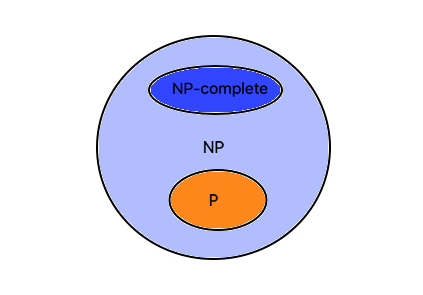
Problems of type P is a subset of NP. This is because problems of type P can be solved quickly as well as its correctness can be verified quickly.
Example: sudoku puzzle, factoring of large numbers
NP-complete problems
A problem X can be said to be NP-complete if any of the exisiting NP-complete problem can be reduced to X in a polynomial time.
General approach to solve NP-complete problems is by using approximations.
Example: Graph coloring problem
Does P = NP?
This is an infamous question that still remains open ended. The NP in ‘Does P = NP?’ actually refers to NP-complete problems. As there is no proof as of now, It is safe to assume that, P != NP.
Comments